Difference Between Xylem and Phloem

pictures for lab Biology 100 with Smith at Minnesota State University, Mankato StudyBlue
The veins that you see in the leaves are actually the xylem and the phloem. These are the vascular tissues. And then you can see they branch off, into becoming smaller and smaller, let me zoom in even further. And you can see them branching off like a network of roads connecting different different parts of the city.

easy diagram of xylem phloem Brainly.in
Unlike xylem, phloem vessels contain cytoplasm, and this goes through the holes in the sieve plates from one cell to the next. Phloem transports sucrose and amino acids up and down the plant.
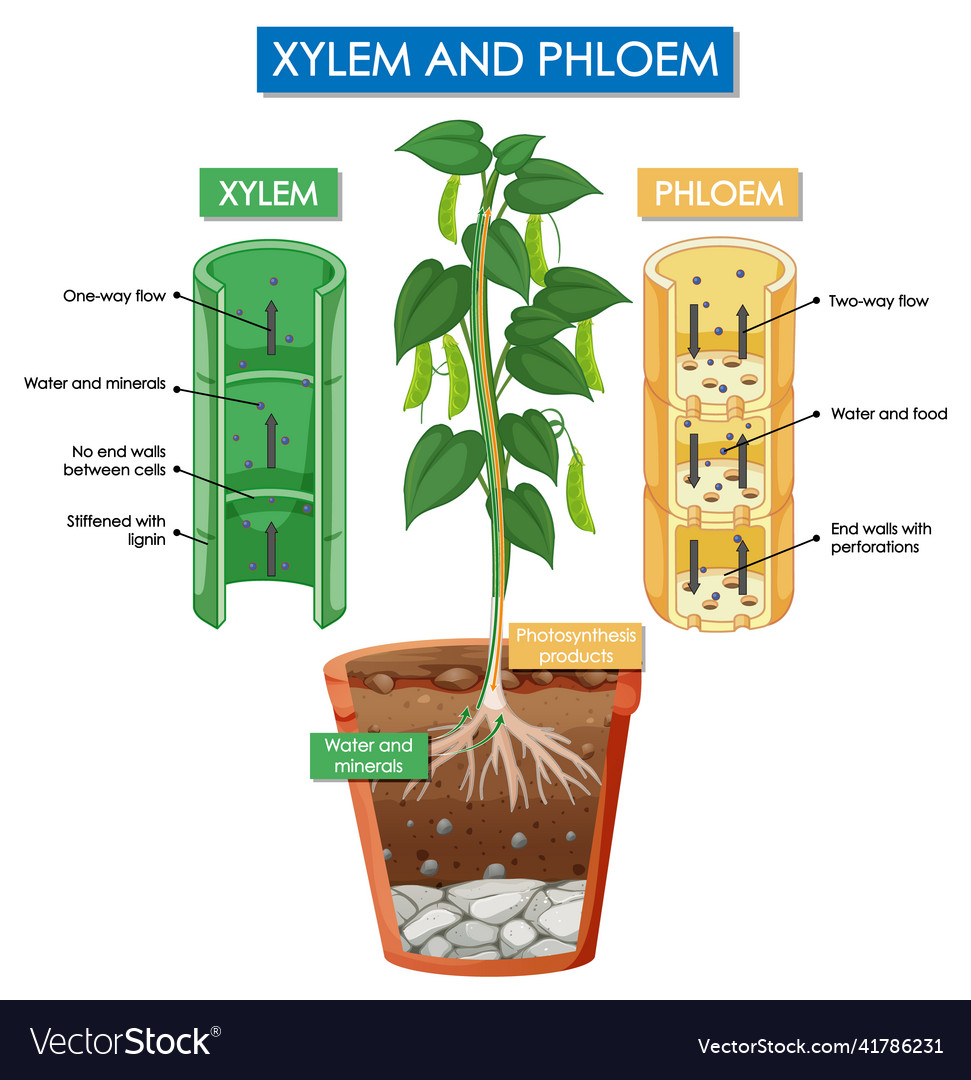
Diagram showing xylem and phloem plant Royalty Free Vector
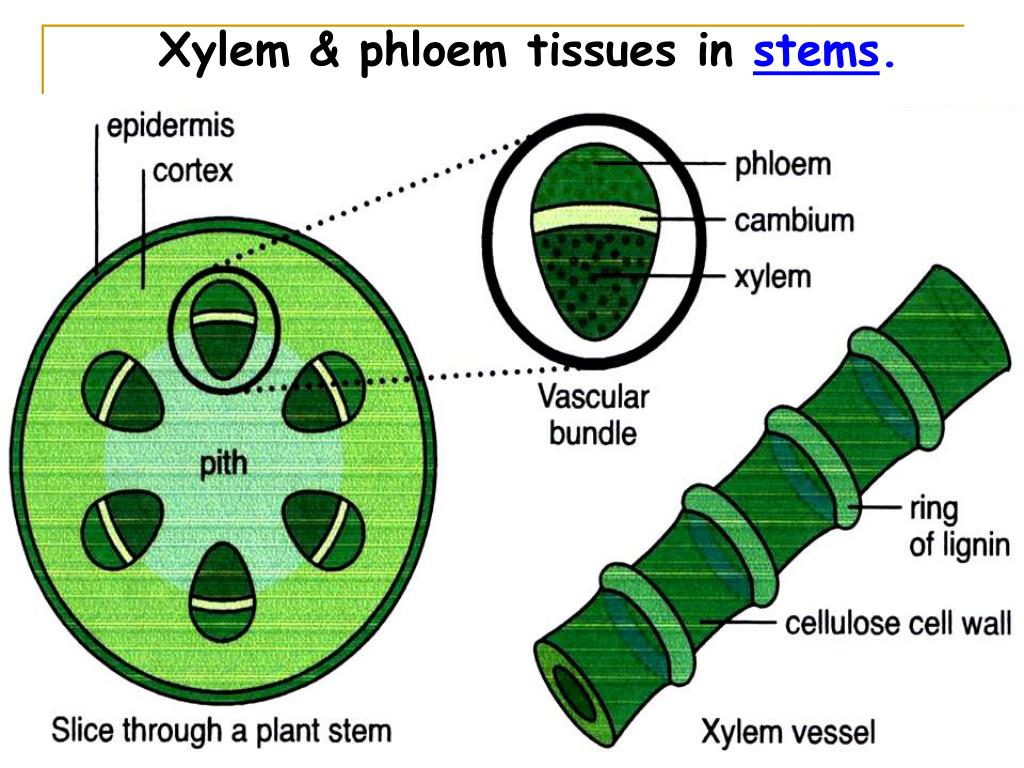
Together, xylem and phloem tissues form the vascular system of plants. Figure 25.4 B. 1: Xylem and phloem: Xylem and phloem tissue make up the transport cells of stems. The direction of water and sugar transportation through each tissue is shown by the arrows. Xylem is the tissue responsible for supporting the plant as well as for the storage.

Diagram showing xylem and phloem in plant 7396776 Vector Art at Vecteezy
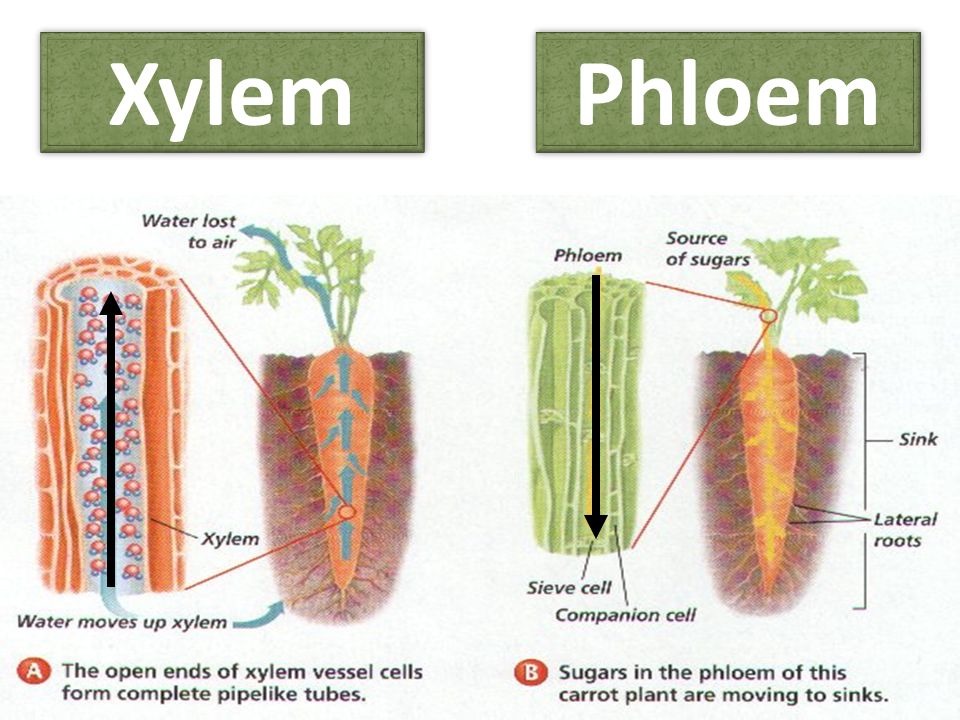
The xylem close xylem vessels Narrow, hollow, dead tubes with lignin, responsible for the transport of water and minerals in plants. transports water and minerals from the roots up the plant stem.
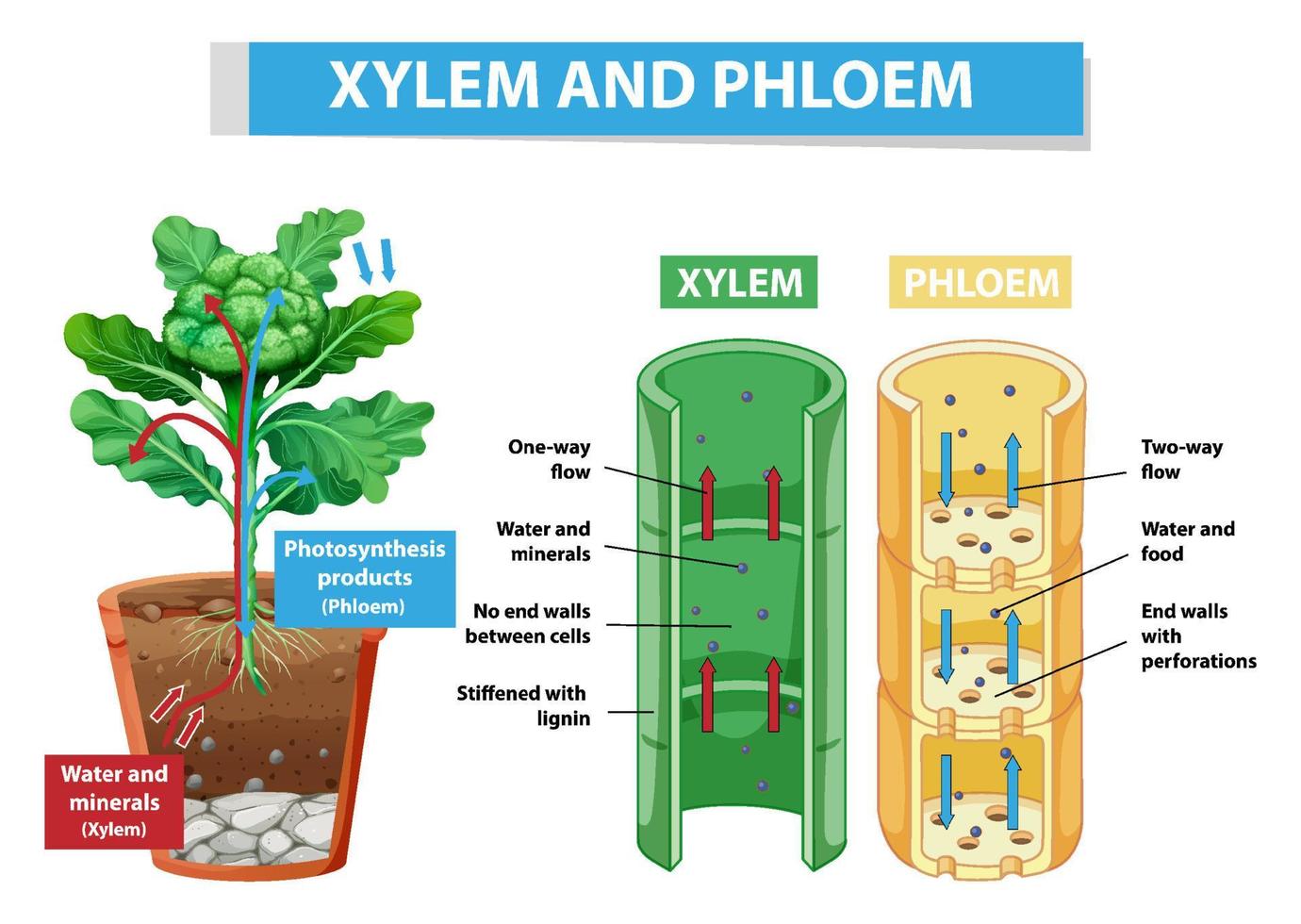
Diagram showing xylem and phloem in plant 7145068 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Xylem and phloem both make up the vascular system of the plant, and work together to form vascular bundles that provide mechanical strength to the plant, but they have important differences. While xylem transports water, phloem transports food and nutrients. (One way to remember this is that phloem and food both begin with an "F" sound.)

Difference Between Xylem and Phloem
The xylem and phloem always lie adjacent to each other (Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\)). In stems, the xylem and the phloem form a structure called a vascular bundle; in roots, this is termed the vascular stele or vascular cylinder. Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\): This light micrograph shows a cross section of a squash (Curcurbita maxima) stem. Each.

Xylem Diagrams
Phloem tissues are found in stems and leaves which later grow in the roots, fruits, and seeds. Composed of: Xylem tissue is composed of xylem vessels, fibers, and tracheids. Phloem tissue is composed of like sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibers, and phloem parenchyma. Fibers: Xylem fibers are robust and longer. Phloem fibers are flexible.
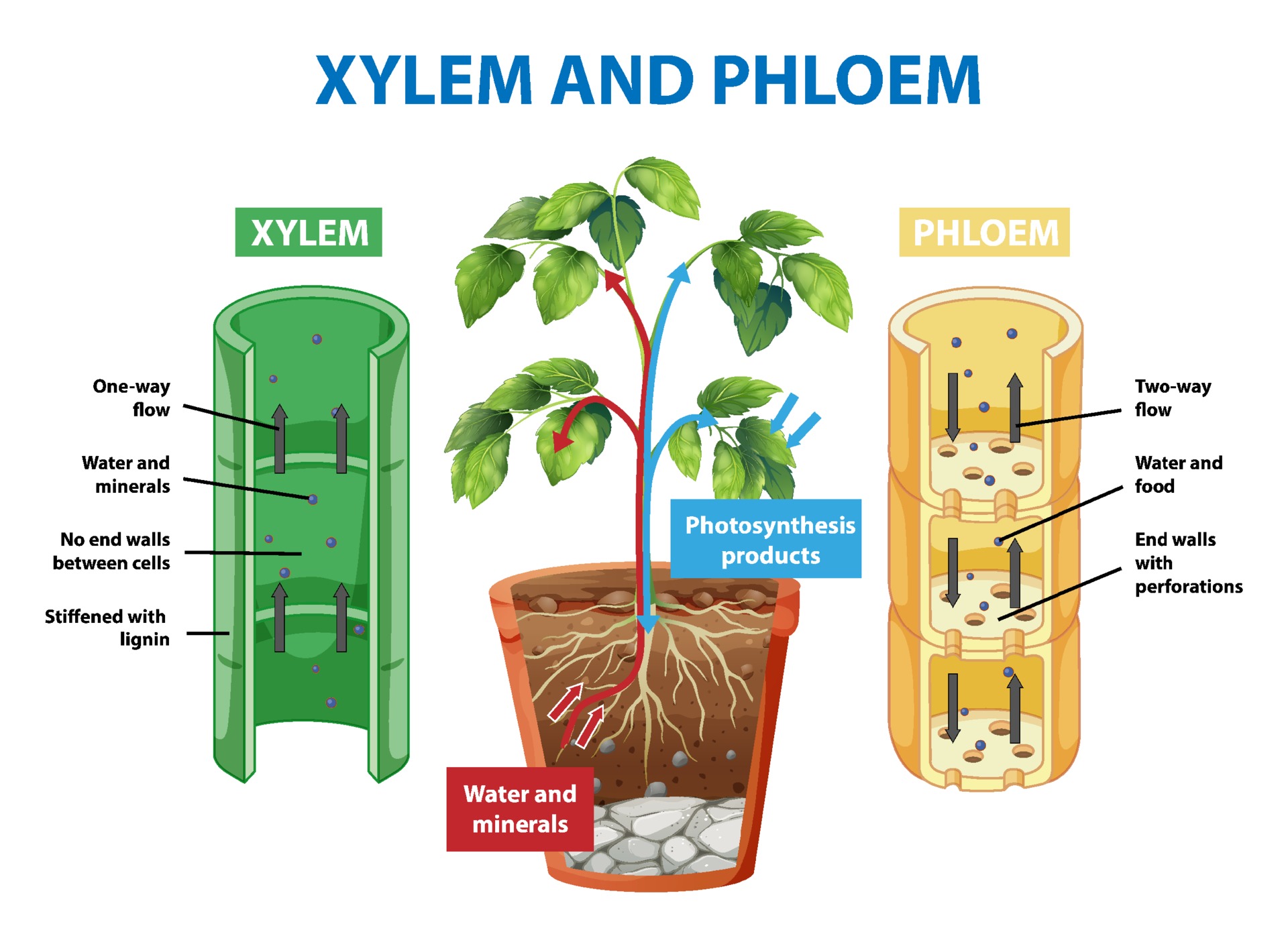
Diagram showing xylem and phloem of plant 1993001 Vector Art at Vecteezy
It is located in the centre of the vascular bundle. It is located on the outer side of the vascular bundle. Xylem fibres are smaller. Phloem fibres are larger. They are present in roots, stems and leaves. They are present in stems and leaves, which later transports and grow in roots, fruits and seeds.
Phloem Diagram diagram geometry
Phloem. The function of phloem tissue in a plant is to:. Transport organic compounds, particularly sucrose, from the source (eg. leaf) to the sink (eg. roots).The transport of these compounds can occur up and down the plant; Phloem is a complex tissue also made up of various cell types; its bulk is made up of sieve tube elements which are the main conducting cells and the companion cells
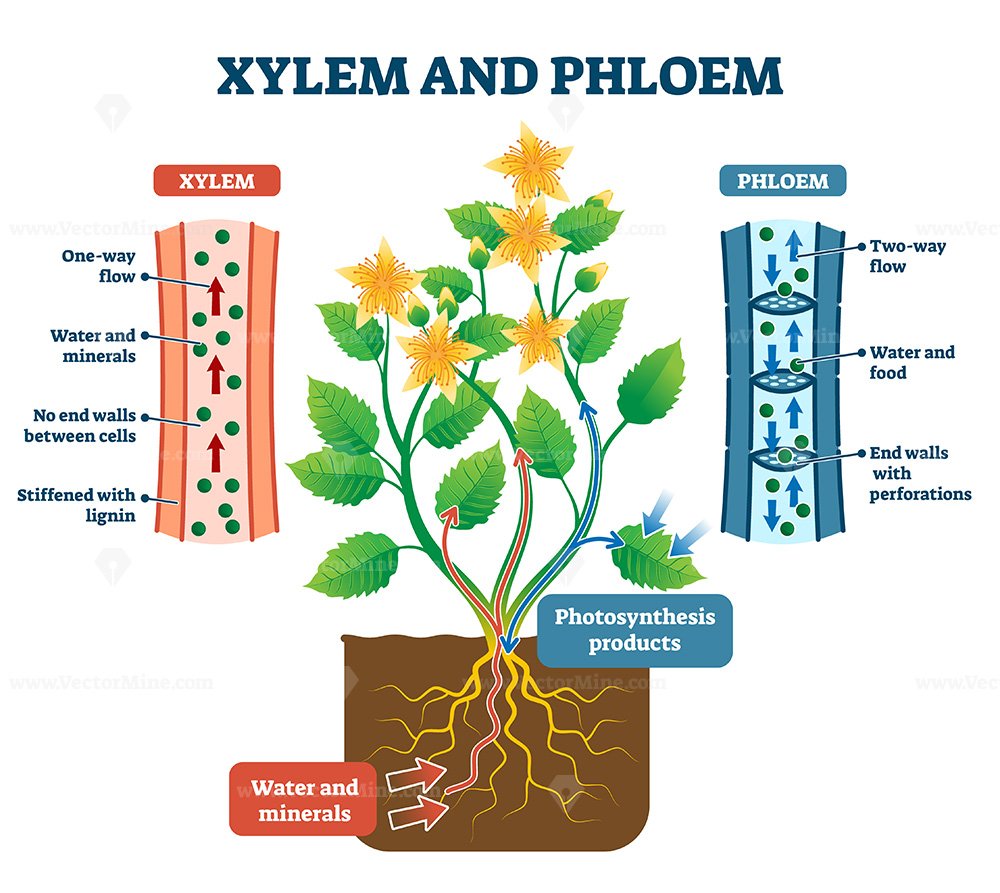
Xylem and phloem water and minerals transportation system outline diagram VectorMine
The xylem and the phloem make up the vascular tissue of a plant and transports water, sugars, and other important substances around a plant. What is commonly referred to as 'sap' is indeed the substances that are being transported around a plant by its xylem and phloem. The separation between plants that have veins and plants that do not is.
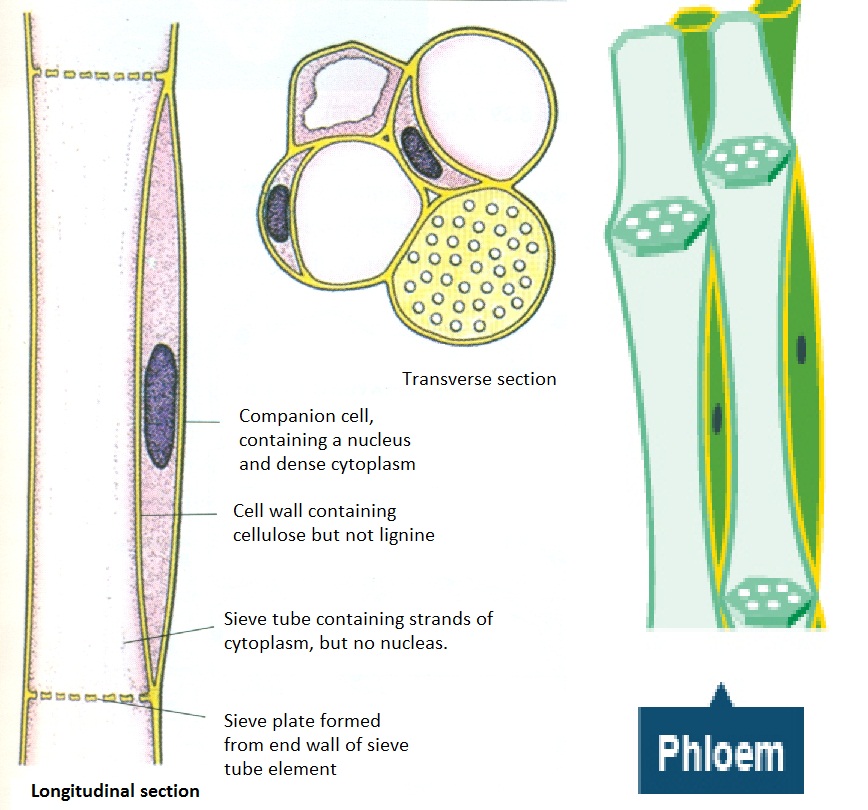
59 Transport in plants functions of xylem and phloem Biology Notes for IGCSE 2014
Phloem sap is an aqueous solution that contains up to 30 percent sugar, minerals, amino acids, and plant growth regulators. The high percentage of sugar decreases Ψ s, which decreases the total water potential and causes water to move by osmosis from the adjacent xylem into the phloem tubes, thereby increasing pressure. This increase in total.
Xylem And Phloem
Xylem and phloem form the vascular system of a plant. Xylem transports water and minerals, while phloem transports food. The vascular system of plants consists of the xylem and phloem. They are somewhat like blood vessels in animals, but plants transport materials using two tissues rather than one. Here is a look at what xylem and phloem are.
PPT state the functions of xylem and phloem. PowerPoint Presentation ID3025578
Transportation. Both phloem and xylem are tubular structures that facilitate easy transportation. In xylem vessels water travels by bulk flow rather than cell diffusion.In phloem, concentration of organic substance inside a phloem cell (e.g., leaf) creates a diffusion gradient by which water flows into cells and phloem sap moves from source of organic substance to sugar sinks by turgor pressure.

Vector Stock Diagram Showing Xylem And Phloem Plant Stock Clip Art The Best Porn Website
Xylem is the dead, permanent tissue that carries water and minerals from roots to all other parts of the plant. The term 'xylem' is derived from the Greek word 'xylon', meaning wood. Phloem, on the other hand, is the living, permanent tissue that carries food and other organic nutrients from leaves to all other parts of the plant.

15 Cell functions Biology Notes for IGCSE 2014
In monocotyledons, unlike the xylem elements, sieve tubes first appeared in the aerial organs, the course being from the leaves to the stem and, lastly, to the roots. Ontogeny of the Sieve Elements: In spite of close ontogenetic resemblance between tracheary elements of xylem and sieve elements of phloem, the latter unlike the former, are living.
Function Of Xylem And Phloem In Leaf
The xylem and phloem carry water and nutrients up and down the length of the stem and are arranged in distinct strands called vascular bundles. The epidermis is a single layer of cells that makes up the dermal tissue covering the stem and protecting the underlying tissue. Woody plants have an extra layer of protection on top of the epidermis.